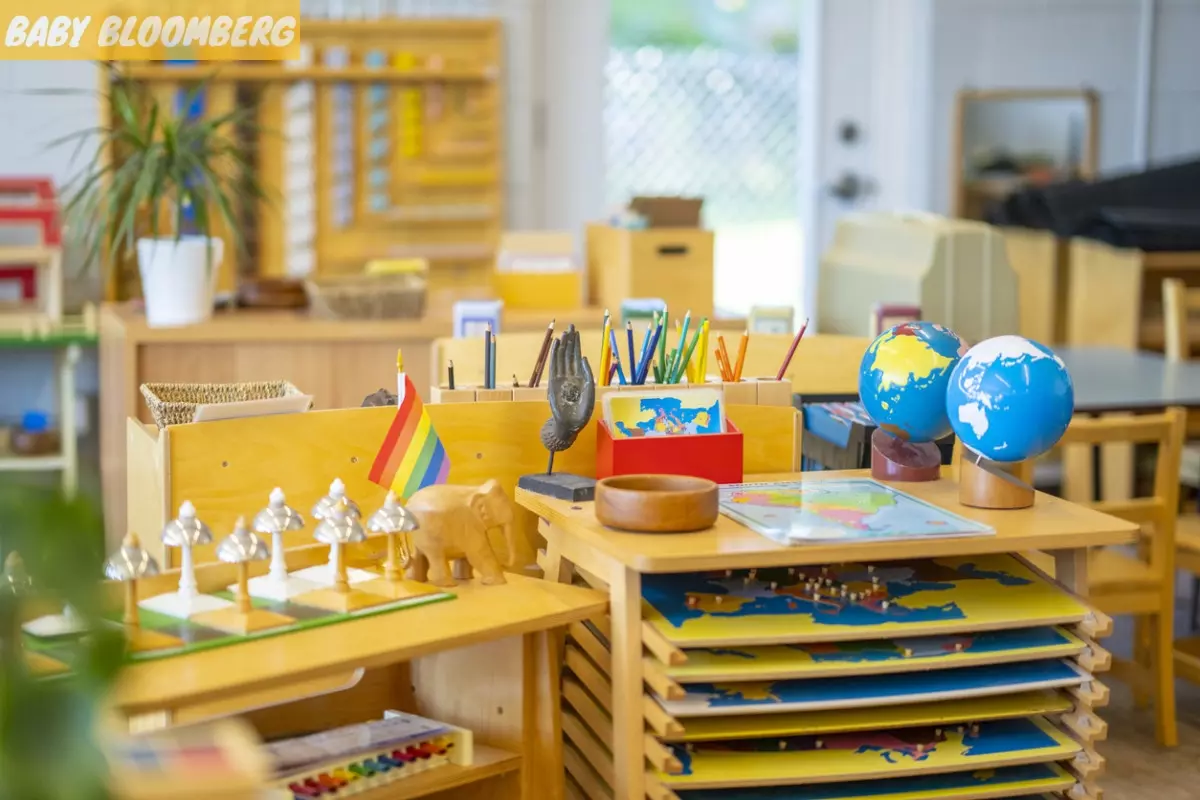
Montessori education, developed by Italian physician and educator Maria Montessori, is an educational approach that emphasizes independence, freedom within limits, and respect for a child’s natural development. This child-centered method recognizes the innate curiosity and desire to learn in children. In Montessori classrooms, children are encouraged to explore and learn at their own pace, following their interests and abilities. The role of the teacher is that of a guide, supporting and observing each child’s learning journey. This article will provide a comprehensive understanding of Montessori education, its principles, and its impact on children’s holistic development.
Montessori Education: Unlocking a Child’s Potential
Montessori education is based on several key principles that shape its unique approach to learning. These principles include:
Independence and Freedom within Limits
Montessori classrooms foster independence by allowing children to choose their activities and work at their own pace. The environment is carefully prepared with age-appropriate materials that encourage exploration and self-directed learning. However, this freedom is accompanied by limits, ensuring that children understand their responsibilities and respect the needs and rights of others.
Respect for Natural Development
Montessori education recognizes that children have their own natural timeline for development. The curriculum is tailored to meet the individual needs and interests of each child, allowing them to progress at their own pace. Montessori classrooms provide an environment that supports the physical, emotional, social, and intellectual development of children.
Hands-on Learning and Sensory Exploration
The Montessori method emphasizes learning through direct experience. Classrooms are equipped with a wide range of hands-on materials that stimulate the senses and promote exploration. These materials are designed to allow children to engage with abstract concepts in a concrete and tangible way, fostering a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Mixed-Age Classrooms
Montessori classrooms typically have mixed-age groupings, where children of different ages learn and work together. This arrangement allows for peer learning and creates a supportive community where older children act as role models and mentors for younger ones. It also promotes the development of social skills and encourages cooperation and collaboration among children.
Montessori Education Through Different Age Levels
Montessori education is not limited to a specific age group and can be implemented from infancy through adolescence. It consists of various levels, each tailored to the developmental needs of children in different age ranges.
Infant and Toddler Programs
Infant and toddler Montessori programs focus on providing a nurturing and stimulating environment for children aged zero to three years. These programs support the development of basic motor skills, language acquisition, and independence. Montessori-trained teachers guide and observe the children’s natural development, providing opportunities for exploration, language development, and practical life skills.
Preschool and Kindergarten
Montessori preschool and kindergarten programs are designed to foster the holistic development of children aged three to six years. In these classrooms, children engage in activities that develop their motor skills, language acquisition, and social skills. The prepared environment encourages independent learning, creativity, and compassion. Montessori materials and activities such as sensorial, practical life, language, and math materials aid children in their cognitive development.
Elementary Classrooms
Elementary Montessori education caters to children aged six to twelve years. These classrooms provide a rich and challenging curriculum that encourages critical thinking, problem-solving, and research skills. Children have the opportunity to explore various subjects, including language arts, mathematics, science, history, and geography. The child-centered approach allows for individualized learning plans and collaborative projects, fostering a deep understanding of the subject matter and a love for learning.
Middle and High School Programs
Montessori education can also extend to the middle and high school years, offering a student-centered approach to learning. These programs aim to develop independent, self-motivated learners who are academically prepared and socially responsible. Students have the opportunity to engage in rigorous academic work, pursue their interests, and contribute to their community through service and experiential learning opportunities.
The Impact of Montessori Education: Fostering Holistic Development
Montessori education aims to foster the holistic development of children, nurturing their intellectual, emotional, social, and physical growth. By providing a child-centered learning environment, Montessori education has several notable impacts:
Independent and Self-Motivated Learners
The emphasis on independence and self-directed learning in Montessori classrooms cultivates a sense of ownership and responsibility in children. They develop strong organizational and time-management skills, enabling them to become independent learners who take initiative and actively engage in their education.
Love for Learning
Montessori education fosters a lifelong love for learning by nurturing children’s natural curiosity and providing them with opportunities for hands-on exploration. Children develop a deep understanding and appreciation for various subjects, inspiring a joy of learning that extends beyond the classroom.
Social and Emotional Development
In mixed-age classrooms, children have the opportunity to interact with peers of different ages and abilities. This fosters the development of social skills, empathy, and cooperation. Montessori classrooms promote a sense of community and respect for others, leading to positive social and emotional development.
Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills
The hands-on nature of Montessori education stimulates critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Children are encouraged to explore, experiment, and find solutions independently. They develop analytical and logical thinking, creativity, and the ability to approach challenges with resilience and perseverance.
Academic Excellence
Montessori education provides a rigorous academic curriculum that prepares children for higher education. The individualized approach allows children to progress at their own pace and explore subjects based on their interests and strengths. Montessori graduates often demonstrate strong academic skills, creativity, and a deep understanding of complex concepts.
FAQs
Q: What are the primary differences between Montessori education and traditional education?
A: The primary differences lie in the approach to learning and the role of the teacher. Montessori education focuses on child-centered learning, where children are encouraged to explore and learn at their own pace. The role of the teacher is that of a guide, observing and supporting each child’s unique learning journey. In traditional education, the curriculum is typically fixed, and teachers play a more directive role in imparting knowledge.
Q: Is Montessori education suitable for all children?
A: Montessori education is suitable for most children; however, it may not be a perfect fit for everyone. Some children thrive in more structured and teacher-directed environments. It is essential to consider a child’s individual needs, learning style, and preferences when choosing an educational approach.
Q: How can parents support Montessori principles at home?
A: Parents can support Montessori principles at home by creating a prepared environment that encourages independence and exploration. Providing open-ended materials and engaging in hands-on activities promotes self-directed learning. Parents can also foster a love for learning by following their child’s interests, engaging in open-ended conversations, and encouraging independent decision-making.
Q: Are there any specific qualifications required to become a Montessori teacher?
A: Montessori teachers undergo specialized training through accredited Montessori training programs. These programs provide in-depth knowledge of Montessori principles and practices, as well as practical experience in implementing the approach in the classroom. Teachers receive certification upon completion of the training.
Q: How can I find a reputable Montessori school?
A: To find a reputable Montessori school, it is recommended to research and visit different schools in your area. Look for schools that are accredited by reputable Montessori organizations such as the American Montessori Society (AMS) or the Association Montessori Internationale (AMI). Consider visiting the schools, observing the classrooms, and talking to teachers and administrators to gain insights into their approach and philosophy.
Q: What are the long-term benefits of Montessori education?
A: Montessori education has several long-term benefits, including fostering independent and self-motivated learners, developing a love for learning, nurturing social and emotional skills, promoting critical thinking and problem-solving abilities, and preparing children for academic success. Montessori graduates often demonstrate strong leadership qualities, adaptability, and a lifelong passion for learning.
Montessori education is a child-centered approach that empowers children to become independent, self-motivated learners. By honoring the natural development of each child and providing a prepared environment, Montessori education fosters holistic growth. Through hands-on exploration, mixed-age groupings, and an emphasis on independence, children develop a love for learning, critical thinking skills, and social and emotional intelligence. Montessori education transcends age boundaries and can be implemented from infancy through adolescence, nurturing the potential of each child and preparing them for a lifetime of success.