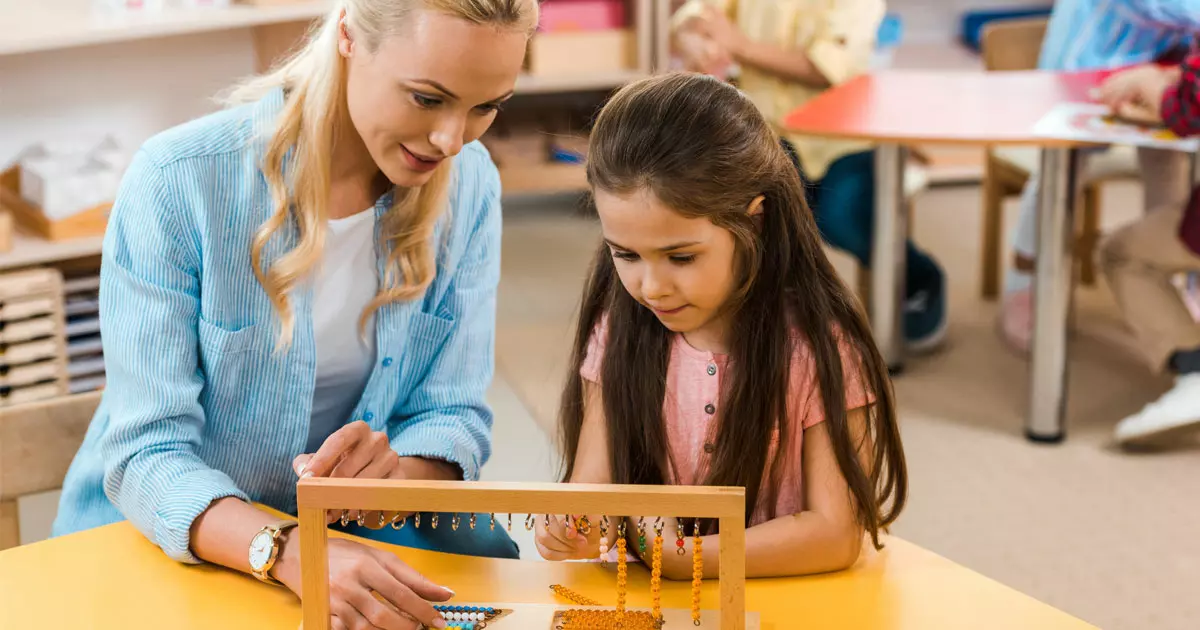
In today’s rapidly evolving world, education plays a vital role in shaping young minds. As educators, it is our responsibility to instill a sense of curiosity, independence, and personal development in our students. Maria Montessori Theory, developed by the Italian physician and educator Maria Montessori, provides a unique approach to education that emphasizes individualized instruction and self-paced learning. This article will explore the key principles and components of Maria Montessori Theory, along with its impact on famous graduates such as Jeff Bezos, founder of Amazon.
1. The Beliefs and Principles underlying Maria Montessori Theory
Maria Montessori Theory is built upon a set of fundamental beliefs and principles about education and child development. At its core, this approach acknowledges that every child is naturally curious and capable of learning independently. By providing an environment that fosters independence, observation, and tailored instruction, Montessori educators empower students to become active learners and critical thinkers.
2. Independence: Fostering Self-Reliance and Autonomy
One of the key principles of Maria Montessori Theory is the emphasis on fostering independence in children. Montessori believed that by encouraging self-reliance and autonomy, young learners develop a strong sense of confidence and self-esteem. This principle is reflected in the organization of the classroom environment, which is carefully designed to allow children to make choices and engage in self-directed activities.
3. Observation: Understanding the Unique Needs of Each Child
In the Montessori classroom, observation plays a vital role in understanding the unique needs and interests of each child. Educators take a step back and carefully observe their students to gain insights into their individual learning styles, strengths, and areas for improvement. This deep understanding allows teachers to tailor instruction and provide the necessary support to maximize each child’s potential.
4. Following the Child: Tailoring Instruction to Individual Abilities
Maria Montessori Theory advocates for a student-centered approach, where educators follow the child’s lead and adapt instruction to their individual abilities. Instead of a one-size-fits-all curriculum, Montessori classrooms provide a wide range of materials and activities that cater to various learning styles and developmental stages. This allows each child to progress at their own pace, ensuring a personalized and fulfilling learning experience.
5. Correcting the Child: Nurturing Self-Discipline and Responsibility
While Montessori education emphasizes independent learning, it also recognizes the importance of guidance and discipline. Rather than punitive measures, correction in the Montessori classroom is focused on nurturing self-discipline and responsibility. Teachers gently guide students towards making informed choices and taking ownership of their actions, fostering a sense of accountability and respect for others.
6. The Prepared Environment: Creating Optimal Learning Spaces
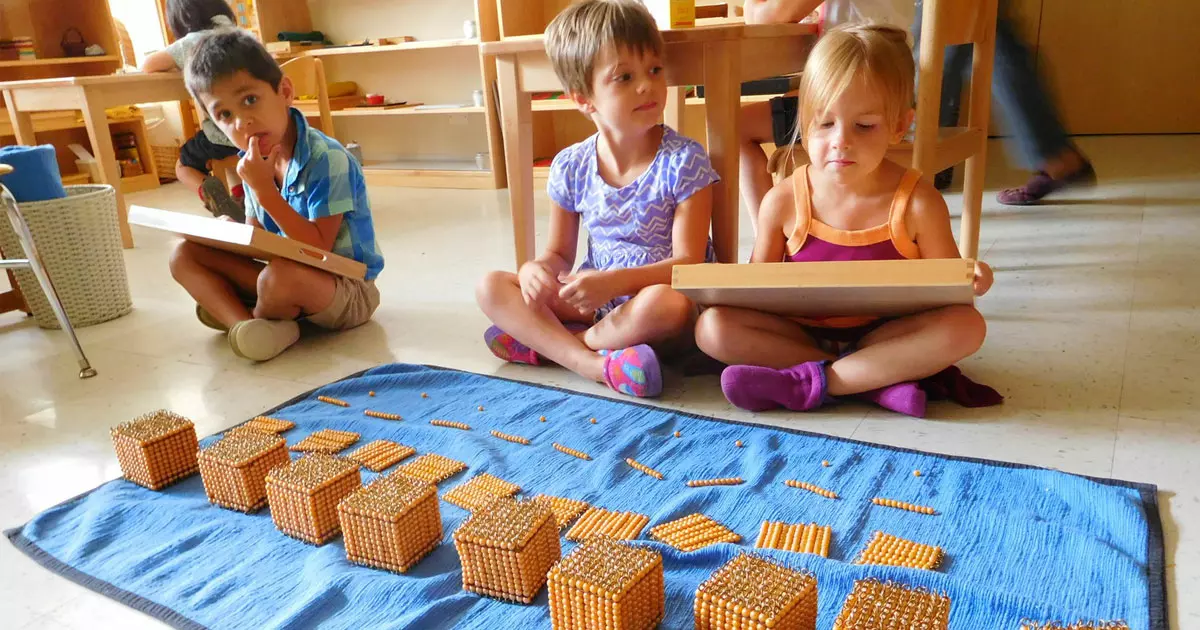
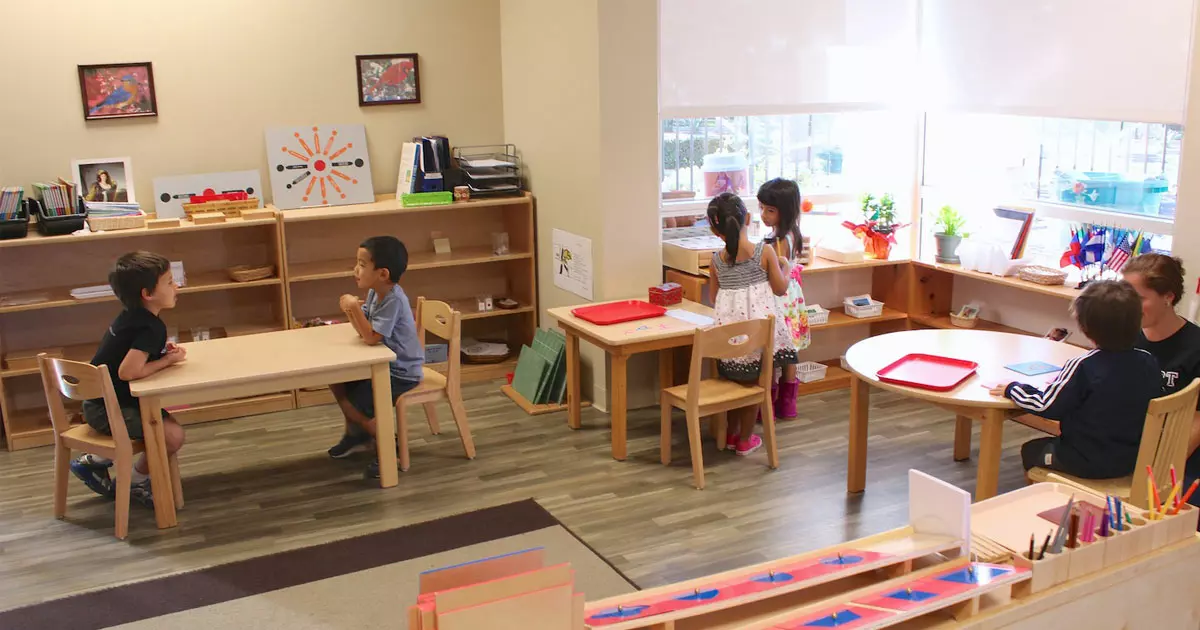
A fundamental aspect of Maria Montessori Theory is the concept of a prepared environment. Montessori classrooms are meticulously designed to create optimal learning spaces that promote exploration, independence, and creativity. Everything from the layout of furniture to the arrangement of learning materials is purposefully organized to encourage hands-on learning and facilitate self-discovery.
7. The Absorbent Mind: Harnessing the Natural Curiosity of Children
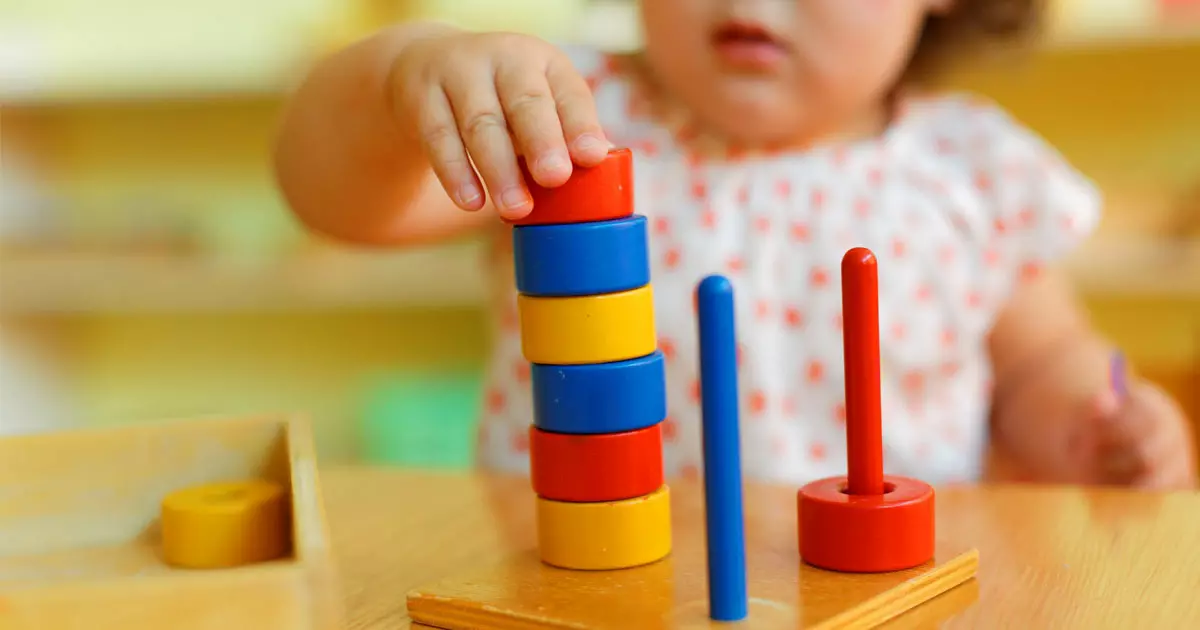
Montessori believed that children possess what she referred to as an absorbent mind, a unique ability to effortlessly soak up knowledge from their environment. This innate curiosity is harnessed through the carefully curated learning materials and activities found in Montessori classrooms. These materials stimulate the senses and encourage children to explore various concepts through their natural inclination towards discovery.
8. Components of Montessori Education
Montessori education comprises several components that work together to create a holistic and effective learning experience. These components include:
8.1 Three-Hour Time Blocks for Activities
In Montessori classrooms, time is structured into three-hour uninterrupted blocks. This extended period allows children to delve deeply into their chosen activities, concentrate on their tasks, and develop a sense of focus and perseverance.
8.2 Mixed-Age Classrooms
Unlike traditional education systems, Montessori classrooms consist of mixed-age groups. This intentional grouping fosters a sense of cooperation, collaboration, and mentoring among the students. Younger children learn from their older peers, while older students reinforce their knowledge by teaching and guiding younger ones.
8.3 Specific Learning Materials and Curricula
Montessori education utilizes a variety of specific learning materials and curricula to facilitate hands-on, experiential learning. These materials are carefully designed to progressively introduce abstract concepts in a concrete and tangible manner. From math manipulatives to language materials, every resource aligns with the developmental stages of the child, ensuring a comprehensive and engaging educational experience.
9. The Development of Maria Montessori Theory
Maria Montessori’s journey towards the development of her educational theory began while she was working with developmentally delayed children in Rome in the late 1890s. It was during this time that she observed the potential for these children to learn and thrive when given the appropriate tools and environment. Drawing from her medical background, Montessori applied scientific principles to develop an educational approach that caters to the unique needs and abilities of each child.
10. Famous Montessori Graduates: Jeff Bezos and Beyond
The impact of Maria Montessori Theory is not limited to the classroom. Numerous successful individuals credit their Montessori education for shaping their character, work ethic, and problem-solving skills. One such notable graduate is Jeff Bezos, the visionary founder of Amazon. Bezos has publicly spoken about how his Montessori education instilled in him a love of learning, the importance of self-directed exploration, and the ability to think outside the box. His experiences and achievements serve as a testament to the effectiveness of Maria Montessori Theory in nurturing independent learners who go on to make significant contributions to society.
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What age group does Montessori education cater to?
A: Montessori education is designed for children from infancy through adolescence, covering the age range of 0 to 18 years.
Q: Are Montessori classrooms suitable for children with special needs?
A: Yes, Montessori classrooms can be adapted to accommodate children with special needs. The individualized approach and focus on self-paced learning make it conducive for students with diverse learning abilities.
Q: Is Montessori education only for privileged children?
A: No, Montessori education is not exclusive to privileged children. Efforts are being made to bring the Montessori approach to a wider range of socio-economic backgrounds, ensuring accessible and equitable education for all.
Q: Are Montessori classrooms too unstructured?
A: While Montessori classrooms provide freedom within limits, they are not devoid of structure. The carefully prepared environment and specific learning materials offer a structure that promotes purposeful exploration and development.
Q: Is Montessori education recognized by traditional academic institutions?
A: Montessori education is recognized and accredited by many traditional academic institutions worldwide. Graduates from Montessori schools often transition seamlessly into mainstream schools and universities.
Q: Can Montessori principles be applied at home?
A: Yes, Montessori principles can be applied in the home environment. Parents can create a prepared environment and provide their children with Montessori-inspired materials and activities to promote independent learning and exploration.
Maria Montessori Theory revolutionized the field of education by emphasizing the importance of individualized instruction and self-paced learning. By embracing principles such as independence, observation, following the child, correcting the child, prepared environment, and absorbent mind, Montessori educators create an environment that nurtures independent learners and fosters personal development. Through mixed-age classrooms, specific learning materials, and three-hour time blocks for activities, students are provided with a holistic educational experience that caters to their unique needs and abilities. The impact of Maria Montessori Theory extends beyond the classroom, with successful individuals like Jeff Bezos attributing their accomplishments to their Montessori education. As we continue to strive for innovative and effective educational methodologies, Maria Montessori Theory stands as a beacon of hope and inspiration, empowering the next generation of independent thinkers and lifelong learners.